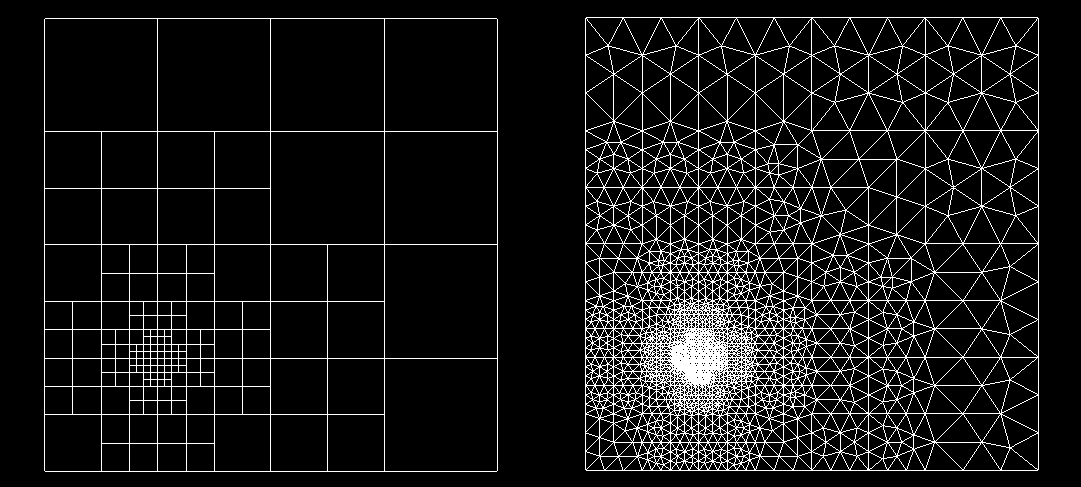
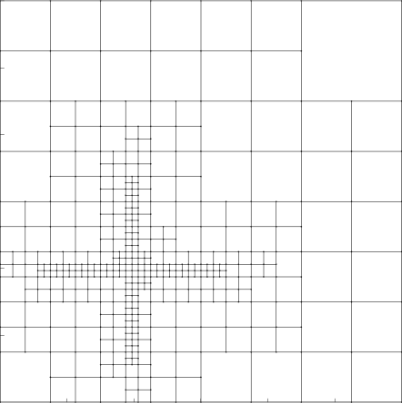
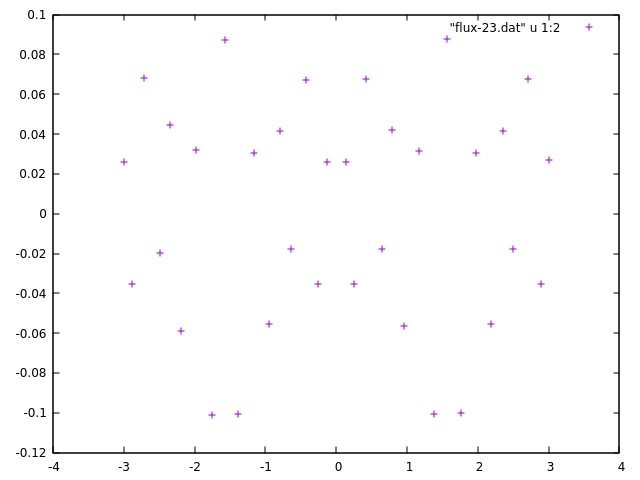
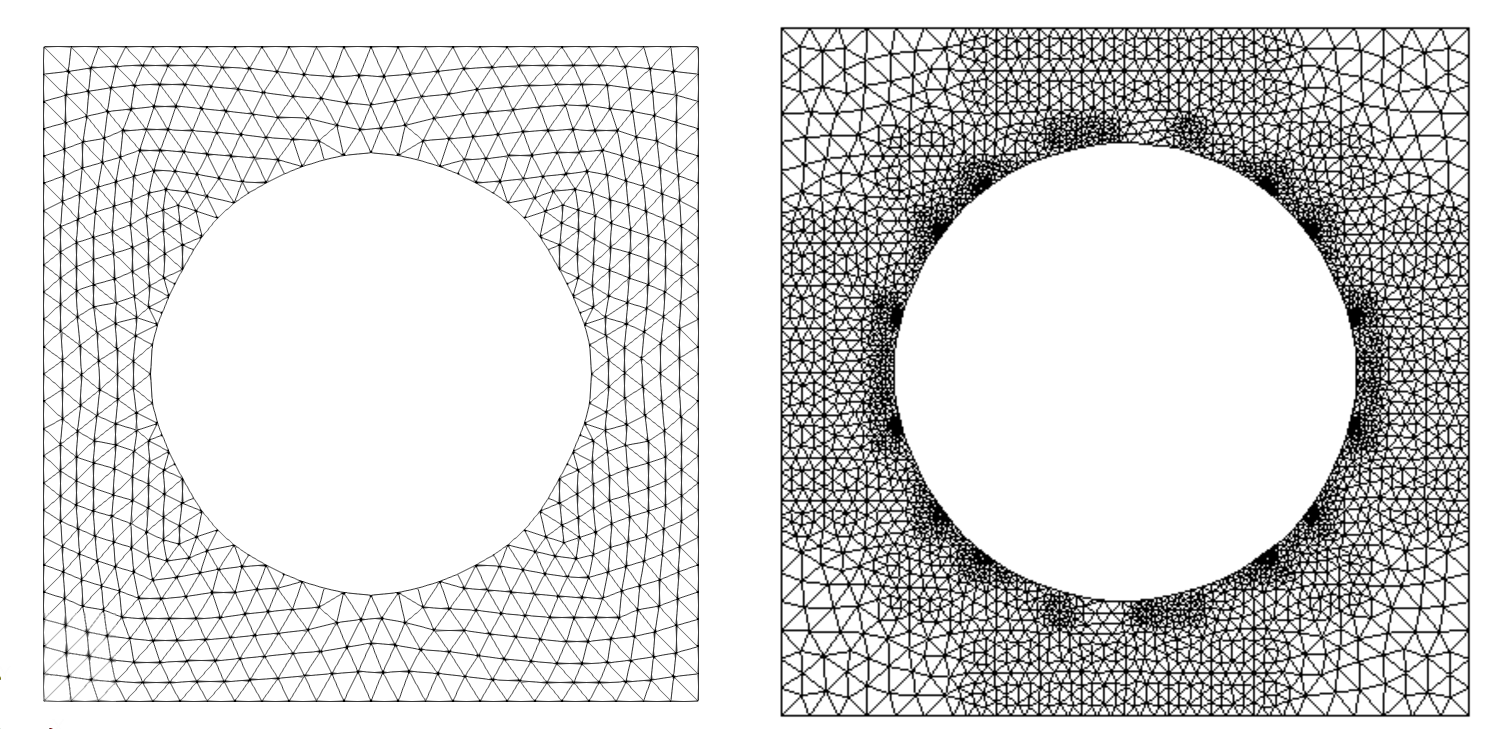
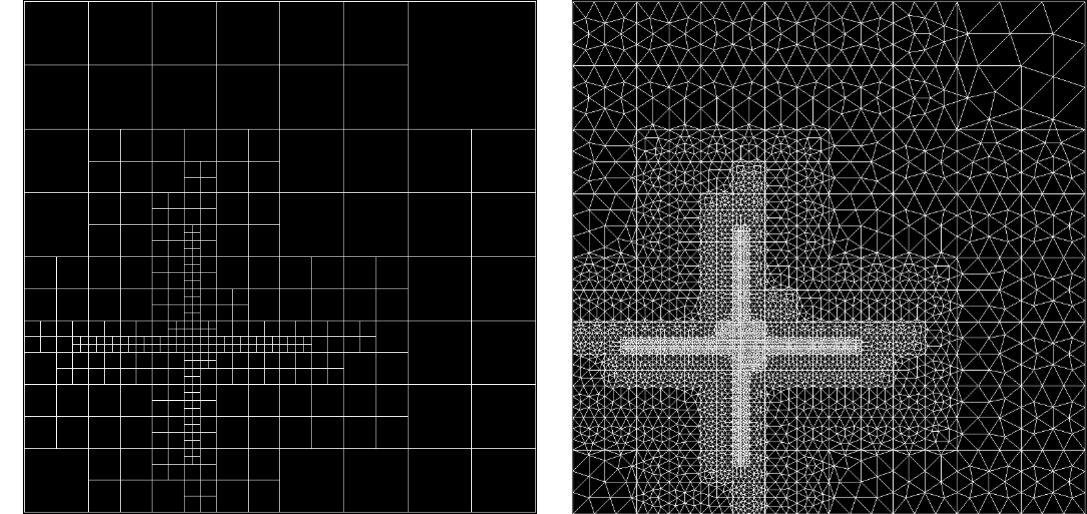
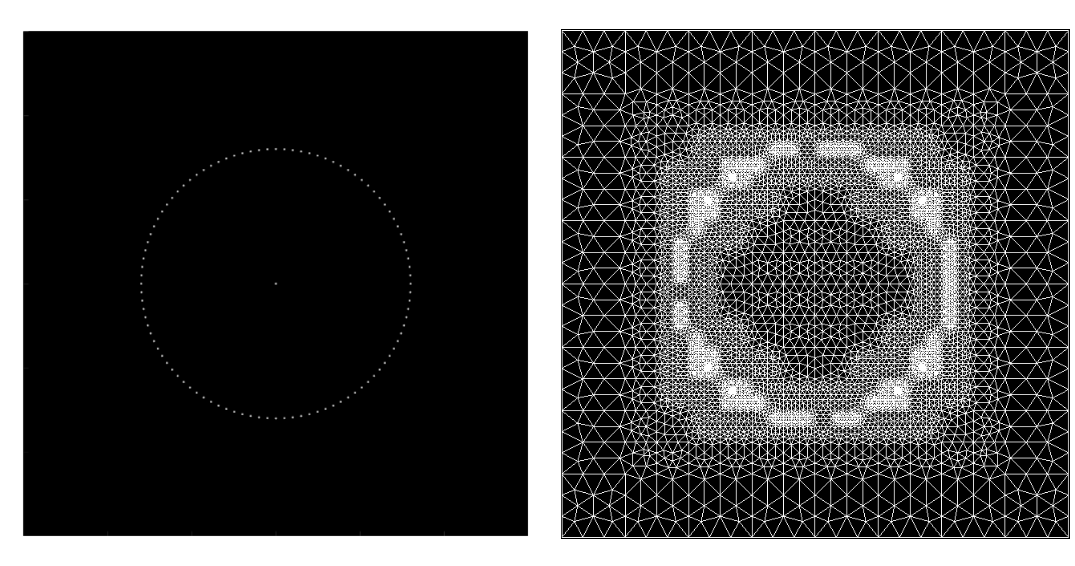
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a numerical method that stitches up local solutions into global ones with the aid of meshes. The accuracy of the solution obtained is directly dependent on the refinement of the mesh used. Erroneous regions of the underlying FE domain can be captured by error functions or point clouds, which can further be used to adaptively refine meshes and improve the solution accuracy.
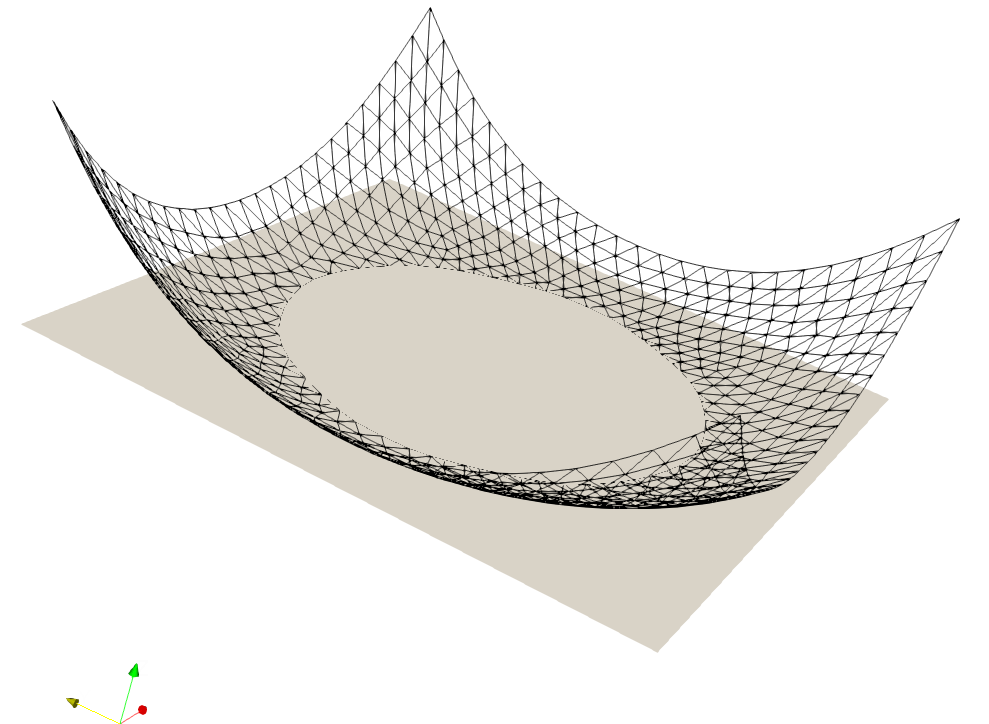
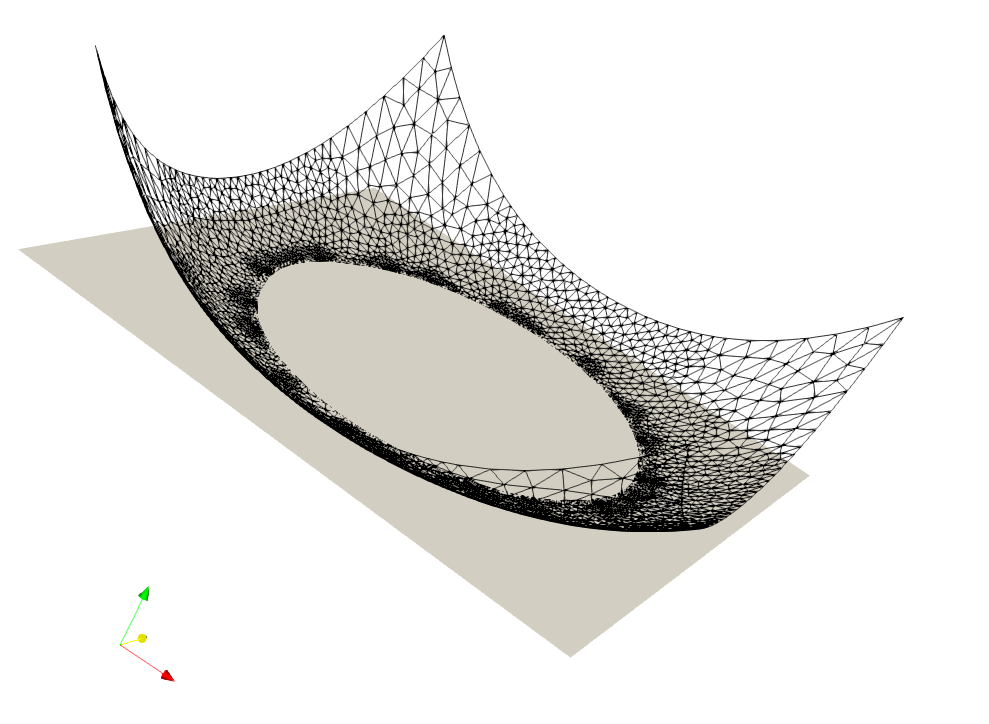
This work implements mesh generation algorithms introduced by Bern, Eppstein and Gilbert, in the paper - Provably Good Mesh Generation. It takes in a user-defined error function or point cloud which quantifies the underlying error, based on which a preliminary quadtree is constructed. Methods of balancing and strong balancing as prescribed by Bern and Eppstein are applied after which stencils are fit, to obtain the final adaptively refined mesh. The implementation was successfully used to demonstrate the reduction of error by solving an obstacle problem. This work was conducted under the guidance of Prof. Ramsharan Rangarajan at the Mechanics and Computation Lab, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science.
Some highlights of this work are -
- This work was used to generate adaptively refined meshes for user-defined error functions and point clouds, with provable guarantees of being good quality triangulations.
- The efficacy of this work was demonstrated by solving an obstacle problem with a regular mesh and an adaptively refined one, followed by a comparison of solution accuracies.
- The code for this work can be found here.